National Early Warning Score (NEWS)
Standardising the assessment of acute-illness severity in the NHS.
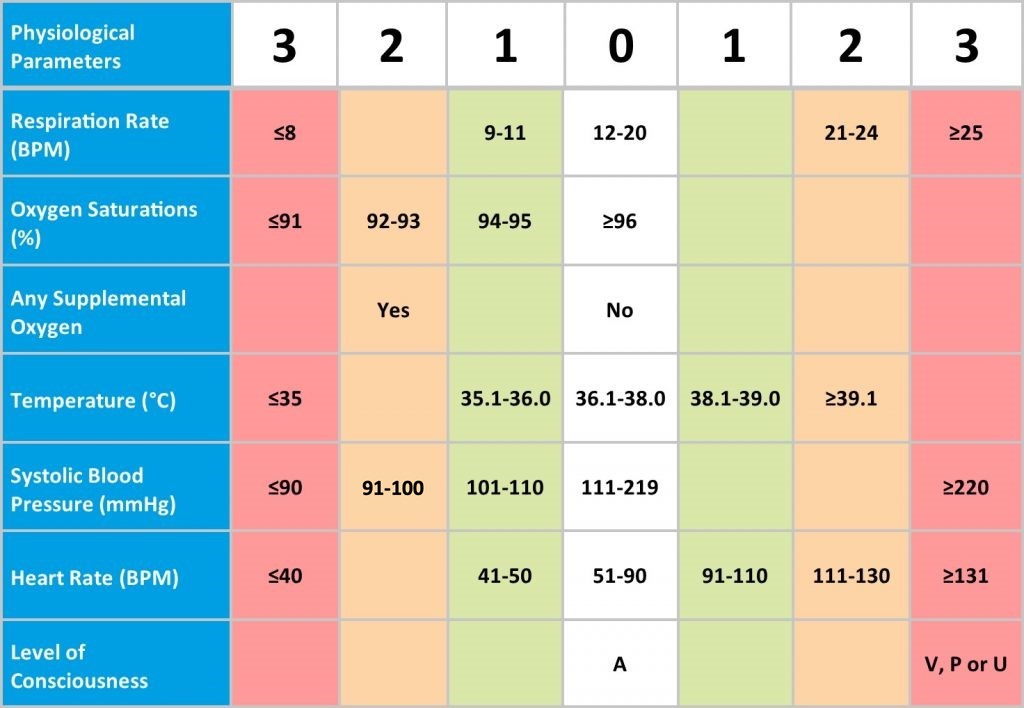
The NEWS, like many existing Early Warning Score systems, is based on a simple scoring system in which a number is allocated to physiological measurements (Vital Signs) already routinely measured in hospital and recorded on the patient clinical chart. The six simple physiological parameters form the basis of the scoring system:
1. Respiratory rate
2. Oxygen saturations
3. Temperature
4. Systolic blood pressure
5. Heart rate
6. Level of consciousness.
A score is allocated to each of these Vital Signs as they are measured and aggregated, and the magnitude of the score reflects how extreme the parameter varies from the norm. The Royal College of Physicians (RCP) advocates standardising the use of a NEWS system across the NHS in order to drive the ‘step change’ required in the assessment and response to acute illness.
The NEWS trigger system aligned to the scale of clinical risk.
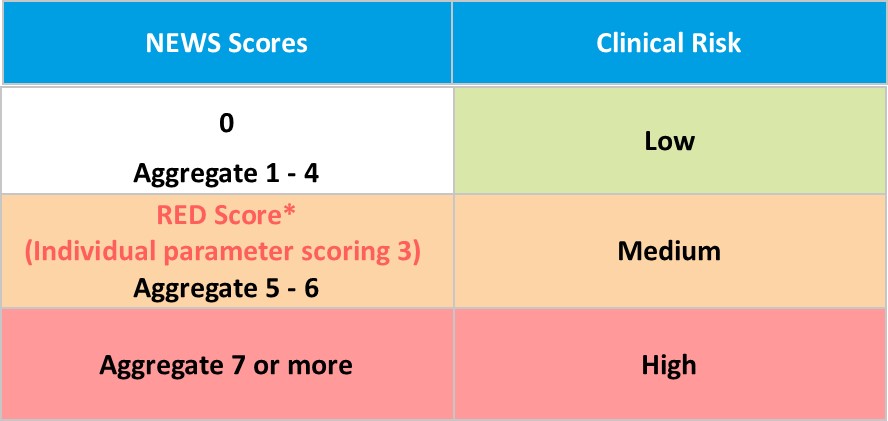
*RED score refers to an extreme variation in a single physiological parameter (i.e. a score of 3 on the NEWS chart, coloured RED to aid identification and represents an extreme variation in a single physiological parameter). The consensus of the NEWS Development and Implementation Group (NEWSDIG) was that extreme values in one physiological parameter (e.g. heart rate 40 beats per minute, or a respiratory rate of 8 per minute or a temperature of 35°C) could not be ignored and on its own required urgent clinical evaluation.
Reproducing this chart: please note that this chart must be reproduced in colour and should not be modified or amended.
The NEWS initiative flowed from the Royal College of Physicians’ NEWSDIG report, and was jointly developed and funded in collaboration with the Royal College of Physicians, Royal College of Nursing, National Outreach Forum and NHS Training for Innovation. (© Royal College of Physicians 2012).
We currently provide one of the NHS England Trusts to provide a Clinical Dashboard for elderly patients with long-term respiratory disease and this is why you will see Five Key Vital Signs from your Health Parameters displayed along the top bar, which can then be used in the NEWS (National Early Warning Score System) used by the NHS to help identify at-risk patients. So if you are caring for another person that has long-term respiratory health condition that affect their heart rate, blood oxygen saturation level (SpO2), systolic blood pressure, temperature and respiration rate, then you can look at their daily readings to help you identify when they may need some extra medical assistance from their healthcare team.
If you would like to know more about this service, please email us on info@aseptika.com.
